
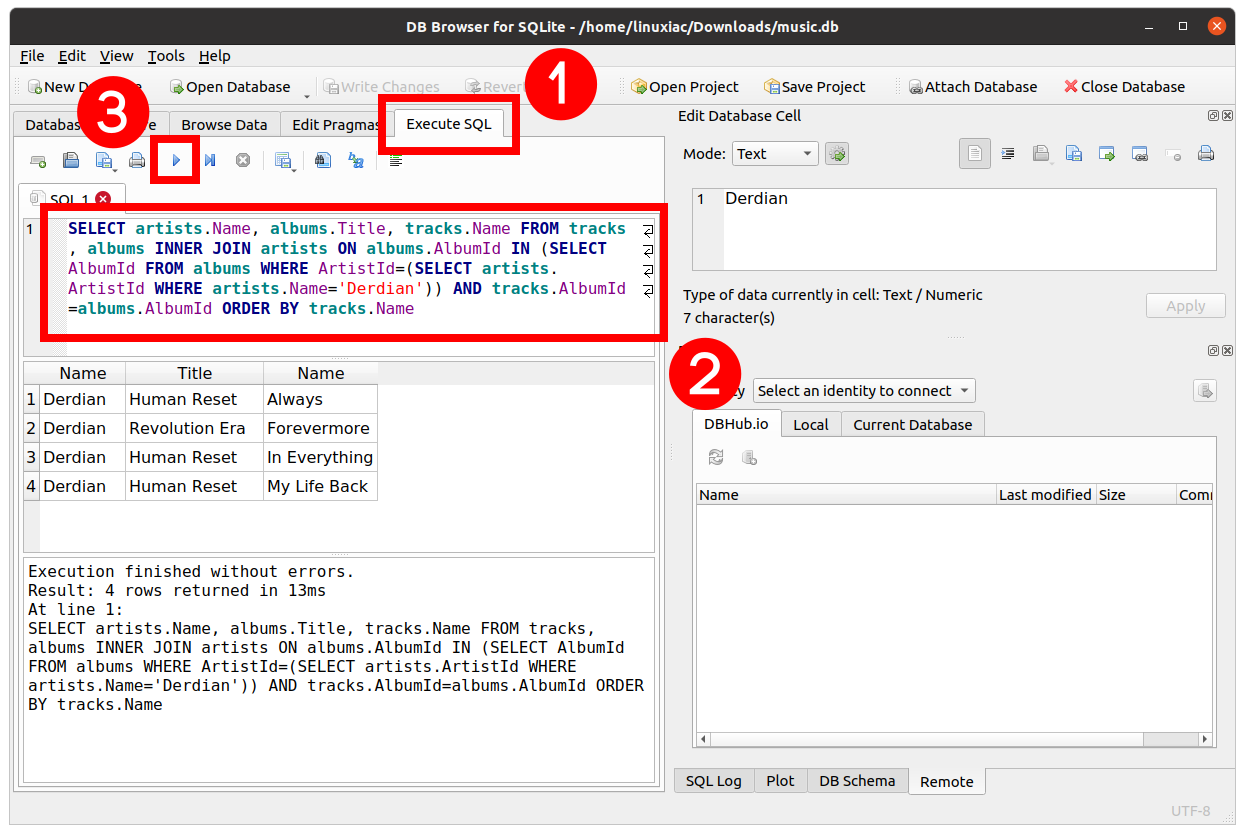
The theoretical maximum size for an SQLite_3 database file is about 140 terabytes typically, the file size limit of the underlying filesystem or hardware is the practical constraint. The page size for a database file is indicated by the 2-byte integer located at an offset of 16 bytes from the beginning of the database file. The size of a page in bytes is a power of two between 56 inclusive. All pages within the same database are the same size.
The main SQLite_3 database file consists of one or more pages. See Appropriate Uses For SQLite for more detail on when SQLite is appropriate and examples of when a client/server SQL database engine would be more appropriate. They are designed to implement a shared repository of enterprise data SQLite is designed to provide local data storage for individual applications. SQLite is not directly comparable to client/server SQL database engines such as MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server.
#Db browser for sqlite extensions software
See Adoption under Sustainability Factors below for examples of the many operating systems and software applications in which it is distributed or used. These features make SQLite_3 a popular choice as an application file format. The database file format, referred to here as "SQLite_3", is cross-platform, transferable between 32-bit and 64-bit systems or between big-endian and little-endian architectures. The engine, and thus the file format, support a full-featured SQL implementation. A complete SQL database with tables, indexes, triggers, and views, is contained in a single disk file.

SQLite is an embedded SQL database engine that requires no configuration and reads and writes directly to ordinary disk files. The code, software, and accompanying documentation have been dedicated to the public domain. Software and associated documentation are available at. SQLite, version 3, is the file format used as the publicly documented native format for the SQLite database engine since June 2004.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
